Identification Method of Natural Graphite and Artificial Graphite
The natural graphite anode material is made of natural flake crystal graphite, which is processed by grinding, spheroidizing, classification, purification and surface, etc. Its high crystallity is formed naturally. And artificial graphite anode material is easy to graphitization carbon such as petroleum coke, needle coke, asphalt coke, calcination at a certain temperature, and then after crushing, grading, high temperature graphitization system, its high crystallinity is formed by high temperature graphitization. It is because of the essential difference in the raw materials and preparation technology that the microstructure, crystal structure, electrochemical performance and processing performance of the two are obviously different.

In terms of microstructure, natural graphite is layered. The SEM profile of natural graphite retains the lamellar structure, and there are a lot of gaps between the lamellar structures. In the process of high temperature graphitization, the crystal structure is rearranged according to the ABAB structure, and the polymerization contraction, and its internal density, no gap.
X-ray diffraction
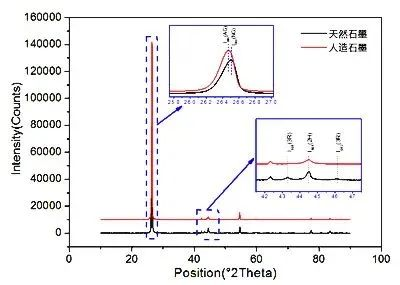
From the perspective of crystal structure, the natural graphite anode material has high crystallinity. In the XRD pattern, its (002) crystal plane diffraction peak Angle is higher, the lamellar structure is complete, the layer spacing is small, and the orientation (I002/I110) is obvious. From the diffraction peak position of (101) crystal plane corresponding to 43-45 degree and the diffraction peak position of (012) crystal plane corresponding to 46-47 degree, It can be seen that natural graphite has obvious 2H phase and 3R phase, while artificial graphite only has 2H phase. The XRD patterns of hexagonal graphite (2H) and rhombohedral graphite (3R) are as follows:

Raman spectroscopy
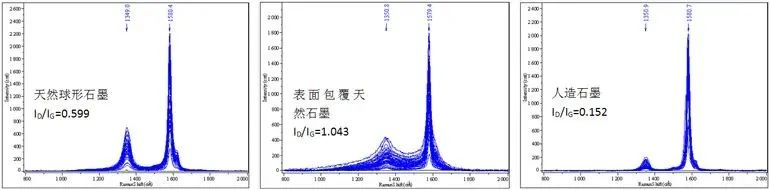
For natural graphite and artificial graphite without graphitization treatment, in addition to the SEM profile, XRD crystal structure diagram and its parameters to distinguish, Raman spectrum test disorder ID/IG is also an effective method to distinguish these two types of graphite. The disorder degree ID/IG of natural spherical graphite is generally 0.4~0.85, the disorder degree ID/IG of natural graphite coated on the surface without graphitization is generally 0.9~1.6, and the disorder degree ID/IG of new modified natural graphite without graphitization is generally 0.2~0.6. The disorder degree OF artificial graphite ID/IG is generally 0.04~0.34. On the whole, the disorder degree ID/IG of natural graphite anode material without high temperature graphitization is larger than that of artificial graphite anode material. The disorder degree ID/IG of the graphitized natural graphite coated on the surface is generally 0.17~0.36, and that of the artificial graphite is generally 0.04~0.34. The disorder degree ID/IG of the graphitized natural graphite and the artificial graphite are in intersection, and Raman test is not an effective method.
result judgment
- Comparison of natural graphite anode materials without high temperature (2400-3300) graphitization treatment and artificial graphite anode materials
(1) SEM cross-section: The SEM cross-section of the natural graphite anode material without high-temperature graphitization has gaps between the flake structures, and the SEM cross-section of the artificial graphite anode material is dense and seamless.
(2) XRD: There are obvious 2H phase and 3R phase in the XRD pattern of natural graphite anode material without high temperature graphitization treatment, and only 2H phase exists in the XRD pattern of artificial graphite anode material.
(3) ID/IG: The disorder ID/IG of the surface-coated natural graphite anode material without high temperature graphitization is generally 0.9~1.6, and the disorder ID/IG of artificial graphite is generally 0.04~0.34.
- Comparison of natural graphite negative material and artificial graphite negative material graphitized at high temperature (2400-3300 )
(1) SEM cross-section: The SEM cross-section of the pure natural graphite anode material treated by high-temperature graphitization has gaps between the flake structures, while the SEM cross-section of the pure artificial graphite anode material has a dense structure and no gaps, and has been subjected to high-temperature graphitization. The SEM cross-sectional view of the composite graphite anode material shows that the voids between the natural graphite flake structures and the artificial graphite dense and seamless structure coexist.


